Let's look at how to deploy Apache Spark, an open-source cluster computing framework for large-scale data processing, to a Docker Swarm Cluster on DigitalOcean. We’ll also look at how to automate the provisioning (and deprovisioning) of machines as needed to keep costs down.
Contents
Project Setup
Clone down the project repo:
$ git clone https://github.com/testdrivenio/spark-docker-swarm
$ cd spark-docker-swarm
Then, pull the pre-built spark image from Docker Hub:
$ docker pull mjhea0/spark:3.0.2
Spark versions 2.0.1, 2.3.3, and 2.4.1 are also available.
The image is about 800MB in size, so it could take a few minutes to download, depending upon your connection speed. While waiting for it to finish, feel free to review the Dockerfile used to build this image along with count.py, which we'll be running through Spark.
Once pulled, set the SPARK_PUBLIC_DNS environment variable to either localhost or the IP address of the Docker Machine:
$ export EXTERNAL_IP=localhost
The
SPARK_PUBLIC_DNSsets the public DNS name of the Spark master and workers.
Fire up the containers:
$ docker-compose up -d --build
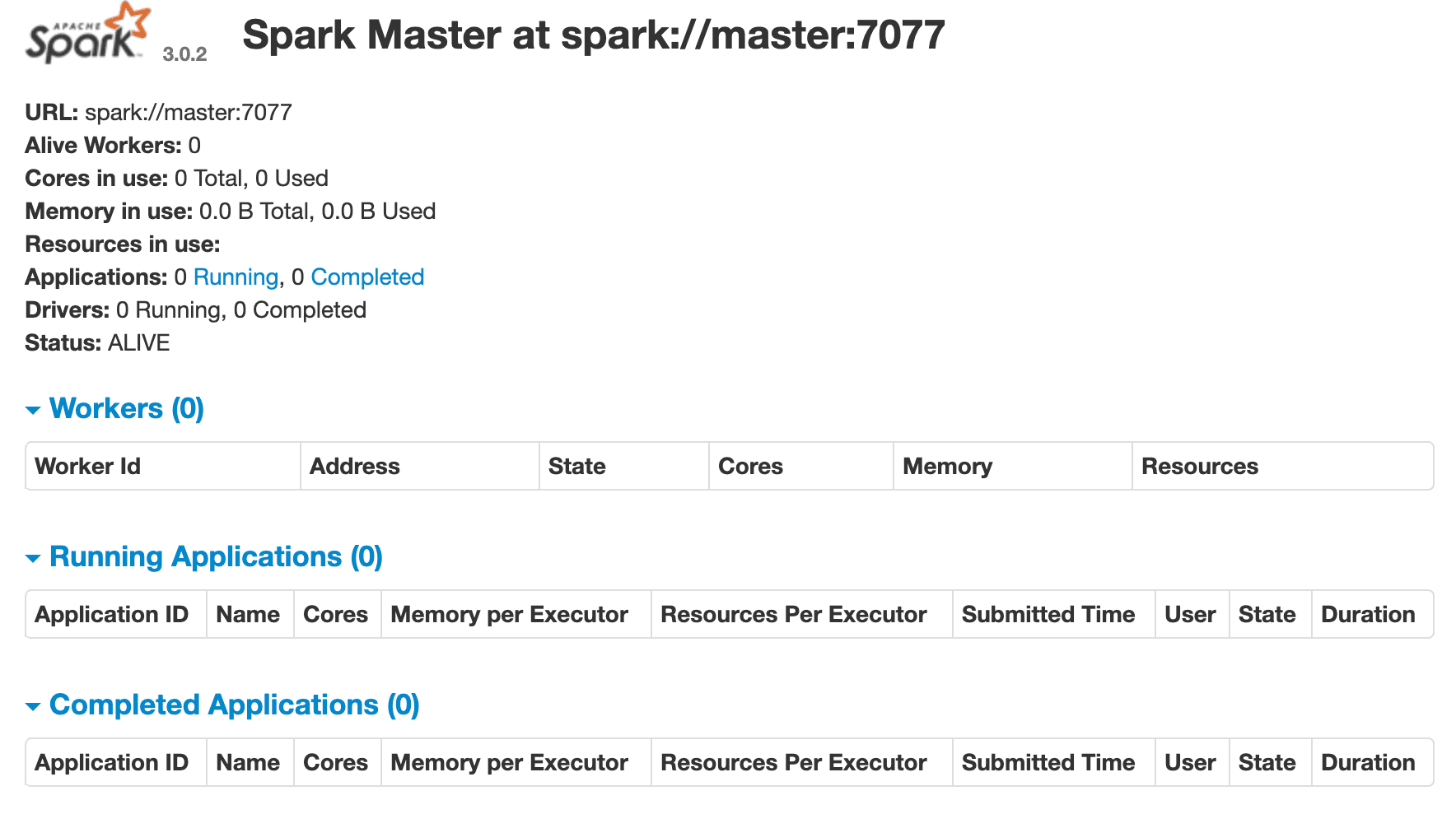
This will spin up the Spark master and a single worker. Navigate in your browser to the Spark master's web UI at http://localhost:8080:
To kick off a Spark job, we need to:
- Get the container ID for the
masterservice and assign it to an environment variable calledCONTAINER_ID - Copy over the count.py file to the "/tmp" directory in the
mastercontainer - Run the job!
Try it out:
# get container id, assign to env variable
$ export CONTAINER_ID=$(docker ps --filter name=master --format "{{.ID}}")
# copy count.py
$ docker cp count.py $CONTAINER_ID:/tmp
# run spark
$ docker exec $CONTAINER_ID \
bin/spark-submit \
--master spark://master:7077 \
--class endpoint \
/tmp/count.py
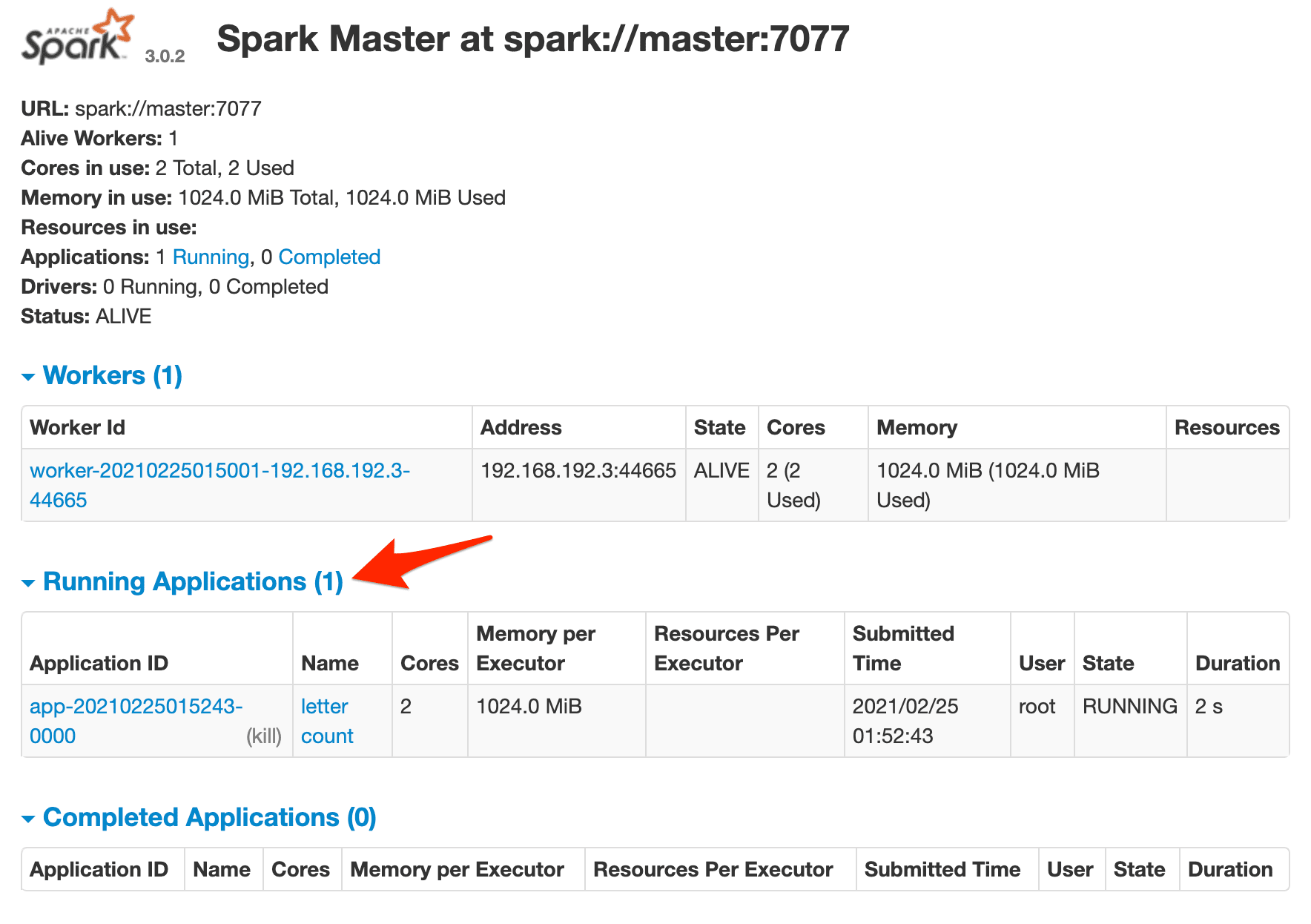
Jump back to the Spark master's web UI. You should see one running job:
And, in the terminal, you should see the outputted Spark logs. If all went well, the output from the get_counts() function from counts.py should be:
{'test': 2}
With that, let's spin up a Swarm cluster!
Docker Swarm
First, you'll need to sign up for a DigitalOcean account (if you don't already have one), and then generate an access token so you can access the DigitalOcean API.
Add the token to your environment:
$ export DIGITAL_OCEAN_ACCESS_TOKEN=[your_digital_ocean_token]
Spin up three DigitalOcean droplets:
$ for i in 1 2 3; do
docker-machine create \
--driver digitalocean \
--digitalocean-access-token $DIGITAL_OCEAN_ACCESS_TOKEN \
--engine-install-url "https://releases.rancher.com/install-docker/19.03.9.sh" \
node-$i;
done
Initialize Swarm mode on node-1:
$ docker-machine ssh node-1 \
-- docker swarm init \
--advertise-addr $(docker-machine ip node-1)
Grab the join token from the output of the previous command, and then add the remaining nodes to the Swarm as workers:
$ for i in 2 3; do
docker-machine ssh node-$i \
-- docker swarm join --token YOUR_JOIN_TOKEN;
done
Drain the Swarm manager:
$ docker-machine ssh node-1 -- docker node update --availability drain node-1
It's a good practice to drain the Swarm manager so that it can't run any containers.
Point the Docker daemon at node-1, update the EXTERNAL_IP environment variable, and deploy the stack:
$ eval $(docker-machine env node-1)
$ export EXTERNAL_IP=$(docker-machine ip node-2)
$ docker stack deploy --compose-file=docker-compose.yml spark
Add another worker node:
$ docker service scale spark_worker=2
Review the stack:
$ docker stack ps spark
You should see something similar to:
ID NAME IMAGE NODE DESIRED STATE CURRENT STATE
uoz26a2zhpoh spark_master.1 mjhea0/spark:3.0.2 node-3 Running Running 23 seconds ago
ek7j1imsgvjy spark_worker.1 mjhea0/spark:3.0.2 node-2 Running Running 21 seconds ago
l7jz5s29rqrc spark_worker.2 mjhea0/spark:3.0.2 node-3 Running Running 24 seconds ago
Point the Docker daemon at the node the Spark master is on:
$ NODE=$(docker service ps --format "{{.Node}}" spark_master)
$ eval $(docker-machine env $NODE)
Get the IP:
$ docker-machine ip $NODE
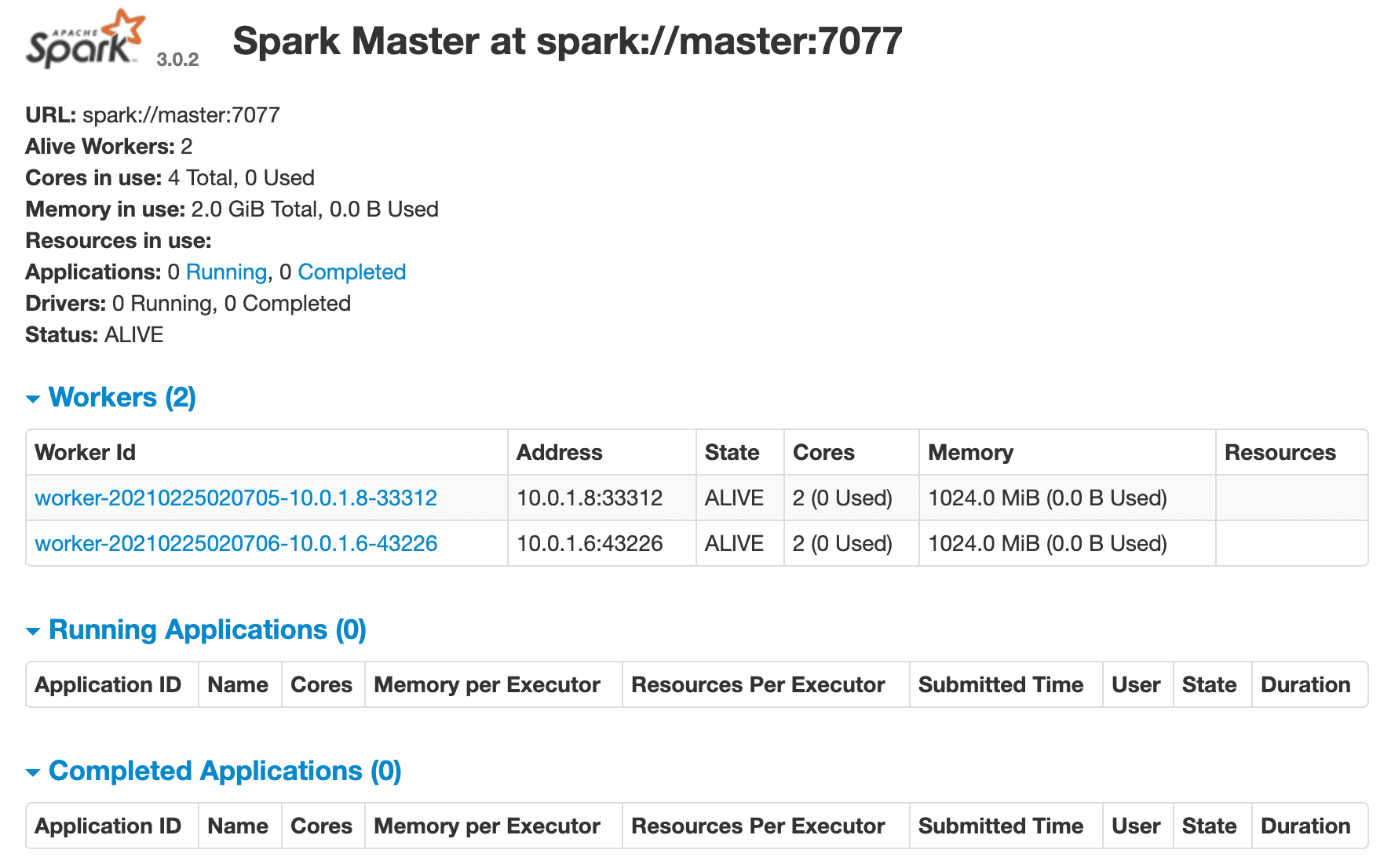
Make sure the Spark master's web UI is up at http://YOUR_MACHINE_IP:8080. You should see two workers as well:
Get the container ID for the Spark master and set it as an environment variable:
$ export CONTAINER_ID=$(docker ps --filter name=master --format "{{.ID}}")
Copy over the file:
$ docker cp count.py $CONTAINER_ID:/tmp
Test:
$ docker exec $CONTAINER_ID \
bin/spark-submit \
--master spark://master:7077 \
--class endpoint \
/tmp/count.py
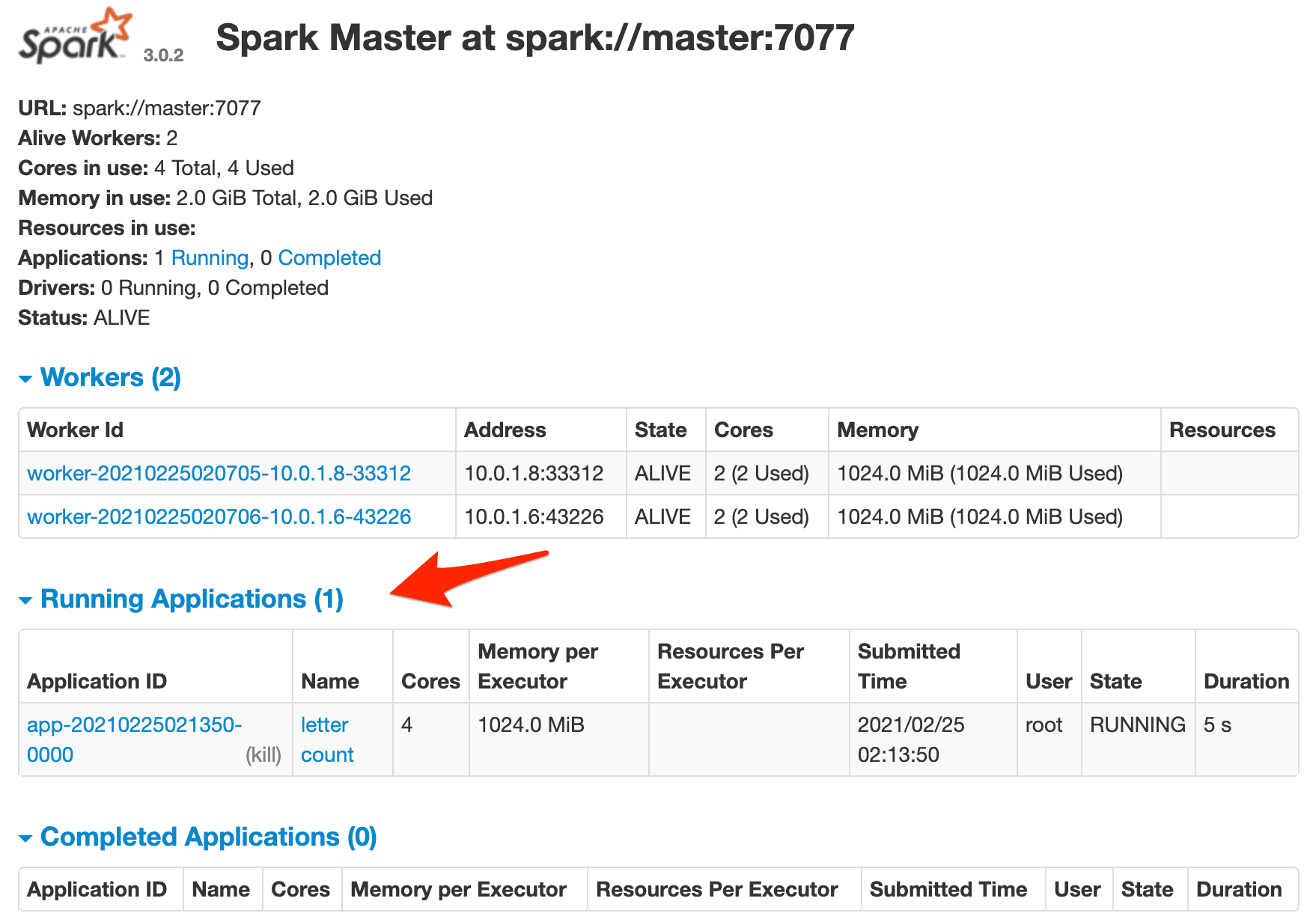
Again, you should see the job running in the Spark master's web UI along with the outputted Spark logs in the terminal.
Spin down the nodes after the job is finished:
$ docker-machine rm node-1 node-2 node-3 -y
Automation Scripts
To keep costs down, you can spin up and provision resources as needed -- so you only pay for what you use.
Let’s write a few scripts that will:
- Provision the droplets with Docker Machine
- Configure Docker Swarm mode
- Add nodes to the Swarm
- Deploy Spark
- Run a Spark job
- Spin down the droplets once done
create.sh:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Spinning up three droplets..."
for i in 1 2 3; do
docker-machine create \
--driver digitalocean \
--digitalocean-access-token $DIGITAL_OCEAN_ACCESS_TOKEN \
--engine-install-url "https://releases.rancher.com/install-docker/19.03.9.sh" \
node-$i;
done
echo "Initializing Swarm mode..."
docker-machine ssh node-1 -- docker swarm init --advertise-addr $(docker-machine ip node-1)
docker-machine ssh node-1 -- docker node update --availability drain node-1
echo "Adding the nodes to the Swarm..."
TOKEN=`docker-machine ssh node-1 docker swarm join-token worker | grep token | awk '{ print $5 }'`
docker-machine ssh node-2 "docker swarm join --token ${TOKEN} $(docker-machine ip node-1):2377"
docker-machine ssh node-3 "docker swarm join --token ${TOKEN} $(docker-machine ip node-1):2377"
echo "Deploying Spark..."
eval $(docker-machine env node-1)
export EXTERNAL_IP=$(docker-machine ip node-2)
docker stack deploy --compose-file=docker-compose.yml spark
docker service scale spark_worker=2
echo "Get address..."
NODE=$(docker service ps --format "{{.Node}}" spark_master)
docker-machine ip $NODE
run.sh:
#!/bin/sh
echo "Getting container ID of the Spark master..."
eval $(docker-machine env node-1)
NODE=$(docker service ps --format "{{.Node}}" spark_master)
eval $(docker-machine env $NODE)
CONTAINER_ID=$(docker ps --filter name=master --format "{{.ID}}")
echo "Copying count.py script to the Spark master..."
docker cp count.py $CONTAINER_ID:/tmp
echo "Running Spark job..."
docker exec $CONTAINER_ID \
bin/spark-submit \
--master spark://master:7077 \
--class endpoint \
/tmp/count.py
destroy.sh:
#!/bin/bash
docker-machine rm node-1 node-2 node-3 -y
Test it out!
The code can be found in the spark-docker-swarm repo. Cheers!
 Michael Herman
Michael Herman