This post details how to deploy Spark on a Kubernetes cluster.
Dependencies:
- Docker v20.10.10
- Minikube v1.24.0
- Spark v3.2.0
- Hadoop v3.3.1
Contents
Minikube
Minikube is a tool used to run a single-node Kubernetes cluster locally.
Follow the official Install Minikube guide to install it along with a Hypervisor (like VirtualBox or HyperKit), to manage virtual machines, and Kubectl, to deploy and manage apps on Kubernetes.
By default, the Minikube VM is configured to use 1GB of memory and 2 CPU cores. This is not sufficient for Spark jobs, so be sure to increase the memory in your Docker client (for HyperKit) or directly in VirtualBox. Then, when you start Minikube, pass the memory and CPU options to it:
$ minikube start --vm-driver=hyperkit --memory 8192 --cpus 4
or
$ minikube start --memory 8192 --cpus 4
Docker
Next, let's build a custom Docker image for Spark 3.2.0, designed for Spark Standalone mode.
Dockerfile:
# base image
FROM openjdk:11
# define spark and hadoop versions
ENV SPARK_VERSION=3.2.0
ENV HADOOP_VERSION=3.3.1
# download and install hadoop
RUN mkdir -p /opt && \
cd /opt && \
curl http://archive.apache.org/dist/hadoop/common/hadoop-${HADOOP_VERSION}/hadoop-${HADOOP_VERSION}.tar.gz | \
tar -zx hadoop-${HADOOP_VERSION}/lib/native && \
ln -s hadoop-${HADOOP_VERSION} hadoop && \
echo Hadoop ${HADOOP_VERSION} native libraries installed in /opt/hadoop/lib/native
# download and install spark
RUN mkdir -p /opt && \
cd /opt && \
curl http://archive.apache.org/dist/spark/spark-${SPARK_VERSION}/spark-${SPARK_VERSION}-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz | \
tar -zx && \
ln -s spark-${SPARK_VERSION}-bin-hadoop2.7 spark && \
echo Spark ${SPARK_VERSION} installed in /opt
# add scripts and update spark default config
ADD common.sh spark-master spark-worker /
ADD spark-defaults.conf /opt/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf
ENV PATH $PATH:/opt/spark/bin
You can find the above Dockerfile along with the Spark config file and scripts in the spark-kubernetes repo on GitHub.
Build the image:
$ eval $(minikube docker-env)
$ docker build -f docker/Dockerfile -t spark-hadoop:3.2.0 ./docker
If you don't want to spend the time building the image locally, feel free to use my pre-built Spark image from Docker Hub: mjhea0/spark-hadoop:3.2.0.
View:
$ docker image ls spark-hadoop
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
spark-hadoop 3.2.0 8f3ccdadd795 11 minutes ago 1.12GB
Spark Master
spark-master-deployment.yaml:
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: spark-master
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: spark-master
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: spark-master
spec:
containers:
- name: spark-master
image: spark-hadoop:3.2.0
command: ["/spark-master"]
ports:
- containerPort: 7077
- containerPort: 8080
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
spark-master-service.yaml:
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: spark-master
spec:
ports:
- name: webui
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
- name: spark
port: 7077
targetPort: 7077
selector:
component: spark-master
Create the Spark master Deployment and start the Services:
$ kubectl create -f ./kubernetes/spark-master-deployment.yaml
$ kubectl create -f ./kubernetes/spark-master-service.yaml
Verify:
$ kubectl get deployments
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
spark-master 1/1 1 1 2m55s
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
spark-master-dbc47bc9-tlgfs 1/1 Running 0 3m8s
Spark Workers
spark-worker-deployment.yaml:
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
metadata:
name: spark-worker
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
component: spark-worker
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: spark-worker
spec:
containers:
- name: spark-worker
image: spark-hadoop:3.2.0
command: ["/spark-worker"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
Create the Spark worker Deployment:
$ kubectl create -f ./kubernetes/spark-worker-deployment.yaml
Verify:
$ kubectl get deployments
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
spark-master 1/1 1 1 6m35s
spark-worker 2/2 2 2 7s
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
spark-master-dbc47bc9-tlgfs 1/1 Running 0 6m53s
spark-worker-795dc47587-fjkjt 1/1 Running 0 25s
spark-worker-795dc47587-g9n64 1/1 Running 0 25s
Ingress
Did you notice that we exposed the Spark web UI on port 8080? In order to access it outside the cluster, let's configure an Ingress object.
minikube-ingress.yaml:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: minikube-ingress
annotations:
spec:
rules:
- host: spark-kubernetes
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: /
backend:
service:
name: spark-master
port:
number: 8080
Enable the Ingress addon:
$ minikube addons enable ingress
Create the Ingress object:
$ kubectl apply -f ./kubernetes/minikube-ingress.yaml
Next, you need to update your /etc/hosts file to route requests from the host we defined, spark-kubernetes, to the Minikube instance.
Add an entry to /etc/hosts:
$ echo "$(minikube ip) spark-kubernetes" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Test it out in the browser at http://spark-kubernetes/:
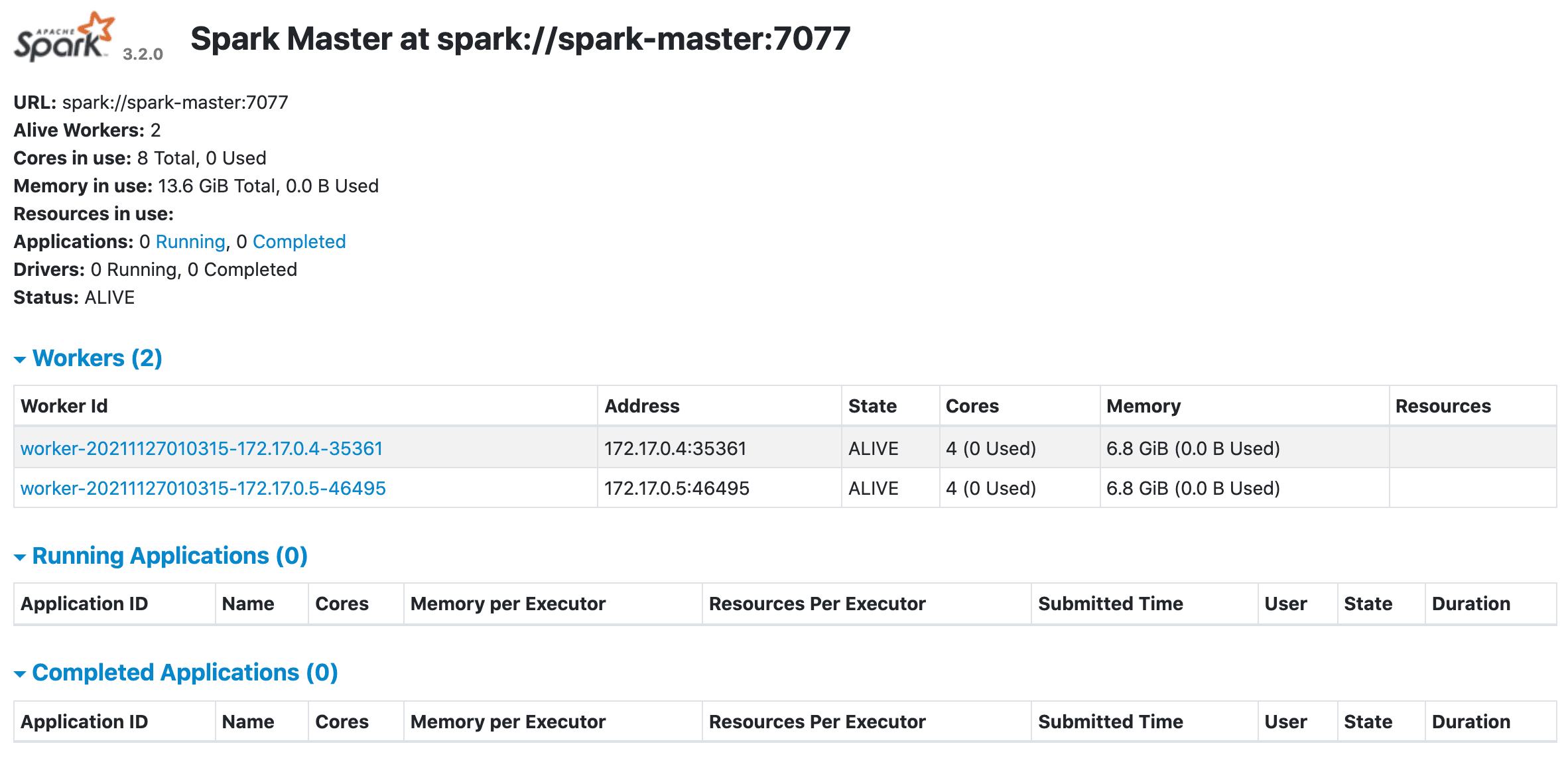
Test
To test, run the PySpark shell from the the master container:
$ kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
spark-master-dbc47bc9-t6v84 1/1 Running 0 7m35s 172.17.0.6 minikube <none> <none>
spark-worker-795dc47587-5ch8f 1/1 Running 0 7m24s 172.17.0.9 minikube <none> <none>
spark-worker-795dc47587-fvcf6 1/1 Running 0 7m24s 172.17.0.7 minikube <none> <none>
$ kubectl exec spark-master-dbc47bc9-t6v84 -it -- \
pyspark --conf spark.driver.bindAddress=172.17.0.6 --conf spark.driver.host=172.17.0.6
Then run the following code after the PySpark prompt appears:
words = 'the quick brown fox jumps over the\
lazy dog the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog'
sc = SparkContext.getOrCreate()
seq = words.split()
data = sc.parallelize(seq)
counts = data.map(lambda word: (word, 1)).reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b).collect()
dict(counts)
sc.stop()
You should see:
{'brown': 2, 'lazy': 2, 'over': 2, 'fox': 2, 'dog': 2, 'quick': 2, 'the': 4, 'jumps': 2}
That's it!
You can find the scripts in the spark-kubernetes repo on GitHub. Cheers!
 Michael Herman
Michael Herman