This tutorial looks at how to debug a containerized Django App in Visual Studio Code (VS Code).
Contents
Objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you should be able to:
- Create a VS Code run configuration to attach to a Docker container
- Modify manage.py to start a debugpy (Python Tools for Visual Studio Debug Server) debug server
- Debug a containerized Django Project in VS Code
Create a Run Configuration
If you haven't already set up a run configuration for your project add a .vscode/launch.json file:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Run Django",
"type": "python",
"request": "attach",
"pathMappings": [
{
"localRoot": "${workspaceFolder}/app",
"remoteRoot": "/usr/src/app"
}
],
"port": 3000,
"host": "127.0.0.1",
}
]
}
Make sure to update the localRoot and remoteRoot values, which VS Code uses to map the source files between your workspace and the filesystem of the remote host. Although these values will differ based on how your project is set up, you can generally get this information from your Docker volume config.
For example, say you have the following config in your Docker Compose file:
volumes:
- ./app/:/usr/src/app/
The local folder path, ./app/, is what localRoot should be set to (e.g., "${workspaceFolder}/app") while remoteRoot should be set to the folder inside the container (e.g., "/usr/src/app"). It's worth noting that this folder inside the container is likely to be your working directory as well:
WORKDIR /usr/src/app
"request": "attach" indicates that we want to connect VS Code's debugger to a process that's already running. In the above config, we tell it to attach to port 3000 on 127.0.0.1. We'll configure debugpy to run on 127.0.0.1:3000 shortly.
When done, click the "Run" icon in the activity bar on the far left. You should now see the Run Django configuration besides the play button in the side bar:
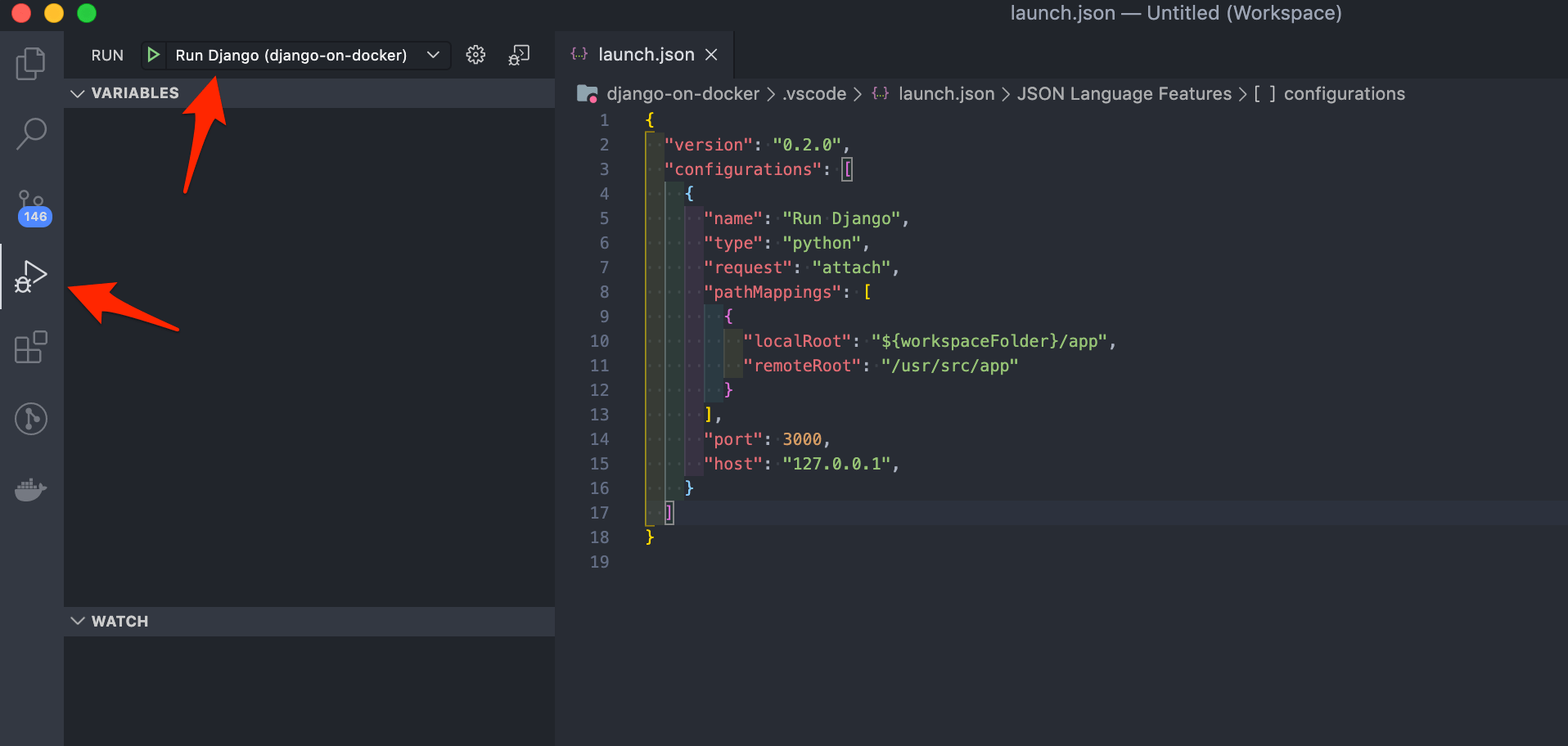
Modify manage.py
With VS Code set up to attach to debugpy, let's integrate it into our app.
To begin with, add the debugpy package to your requirements file:
debugpy==1.5.1
Since debugpy runs alongside the Django app, we'll need to configure it to run inside our manage.py file:
from django.conf import settings
if settings.DEBUG:
if os.environ.get('RUN_MAIN') or os.environ.get('WERKZEUG_RUN_MAIN'):
import debugpy
debugpy.listen(("0.0.0.0", 3000))
print('Attached!')
Your file will look something similar to:
#!/usr/bin/env python
"""Django's command-line utility for administrative tasks."""
import os
import sys
def main():
os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'core.settings')
# start new section
from django.conf import settings
if settings.DEBUG:
if os.environ.get('RUN_MAIN') or os.environ.get('WERKZEUG_RUN_MAIN'):
import debugpy
debugpy.listen(("0.0.0.0", 3000))
print('Attached!')
# end new section
try:
from django.core.management import execute_from_command_line
except ImportError as exc:
raise ImportError(
"Couldn't import Django. Are you sure it's installed and "
"available on your PYTHONPATH environment variable? Did you "
"forget to activate a virtual environment?"
) from exc
execute_from_command_line(sys.argv)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Here, we first determine if the project is running in DEBUG mode. If so, we then make sure that the debugger is not attached if it's a reload of Django (if you change some code while the server is running).
The debugpy.listen() method starts the debug server. You can also block execution until the debugger is attached with wait_for_client():
from django.conf import settings
if settings.DEBUG:
if os.environ.get('RUN_MAIN') or os.environ.get('WERKZEUG_RUN_MAIN'):
import debugpy
debugpy.listen(("0.0.0.0", 3000))
debugpy.wait_for_client()
print('Attached!')
Since debugpy will run on port 3000, you need to expose that port to the host. If you're using Docker Compose, you can expose the port like so:
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
build: ./app
command: python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
volumes:
- ./app/:/usr/src/app/
ports:
- 8000:8000
- 3000:3000
If you're not using Compose, make sure to expose the ports when you run the container:
$ docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 3000:3000 web
Debug the Containerized Django App
After you build the new image to install debugpy, spin up the new container.
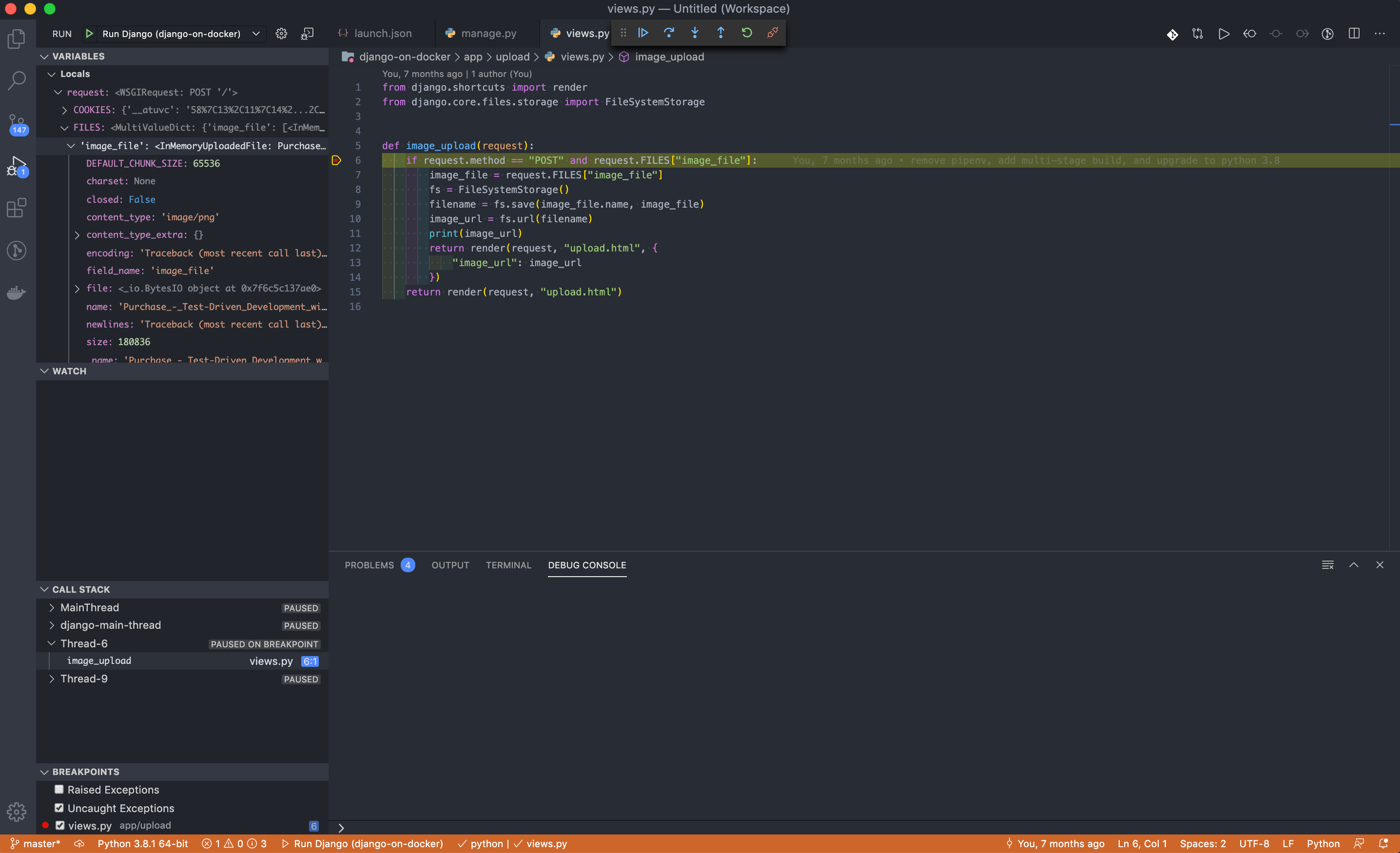
Set a breakpoint somewhere in your code. Then in VS Code open the "Run" view again and make sure the Run Django configuration that we previously created is selected. Click the play button to start the debugging session.
You should now be able to get to the breakpoint and start debugging the Django app running inside the Docker container.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we've shown you how to configure VS Code for debugging a Django App running inside of Docker.
TIP: If you're using Python 3.7 or later, debugpy also supports Python's
breakpoint()function.
 J-O Eriksson
J-O Eriksson